Electricity by Source in the United States
Introduction
This post is about electricity generation in the United States. We will look at the sources used to produce electricity. The data is provided by the U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) which publishes reports and statistics related to the energy sector in the United States.
The specific dataset used in this post was extracted from the page Net Generation by Energy Source on the EIA’s website. The data presented in the emissions table was taken from EIA’s Monthly Report.
Dataset
The net generation dataset contains the electricity production in the United States by source.
The sources included are classified as: Coal, Petroleum Liquids, Petroleum Coke, Natural Gas, Other Gas, Nuclear Hydroelectric Conventional, Solar, Other Renewables, Hydroelectric Pumped, Storage, Other.
From the website:
Renewable Sources include wood, black liquor, other wood waste, biogenic municipal solid waste, landfill gas, sludge waste, agriculture byproducts, other biomass, geothermal, solar thermal, photovoltaic energy, and wind.
Other includes non-biogenic municipal solid waste, batteries, hydrogen, purchased steam, sulfur, tire-derived fuel, and other miscellaneous energy sources.
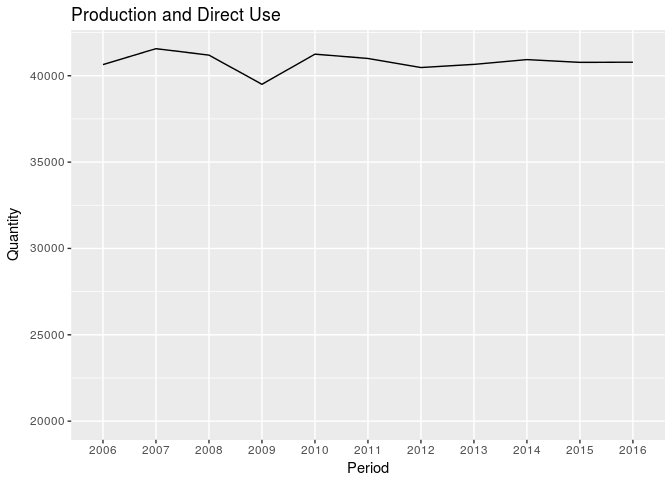
Total Generation
The generation of electricity has been mostly flat in the past ten years except for a small dip in 2009 due to the Great Recession. This is interesting because the dip in lost output (GDP) during the great recession was a lot deeper than the one shown on this graph.
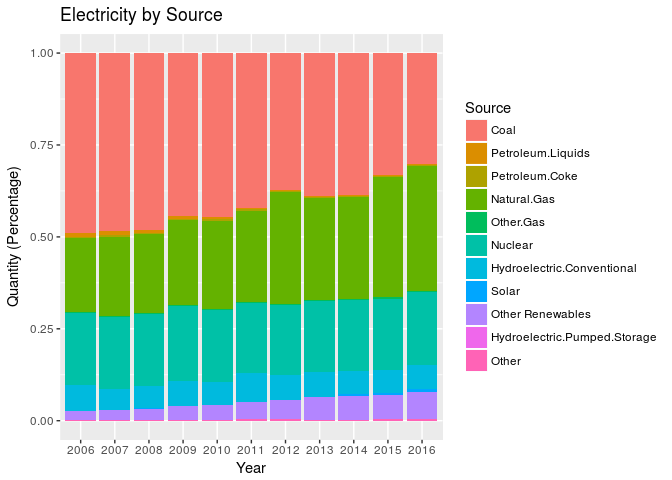
Generation by Source
The following graph shows how the generation by source changed over time. Here are the trends over a ten year period ending in 2016:
- Coal has decreased from about 50% to about 30%.
- Natural Gas has increased from about 20% to above 30%
- Other Renewables increased from about 2% to about 5%
- Solar went from almost zero (0.01%) to almost 1%
- Nuclear has been constant around 20%
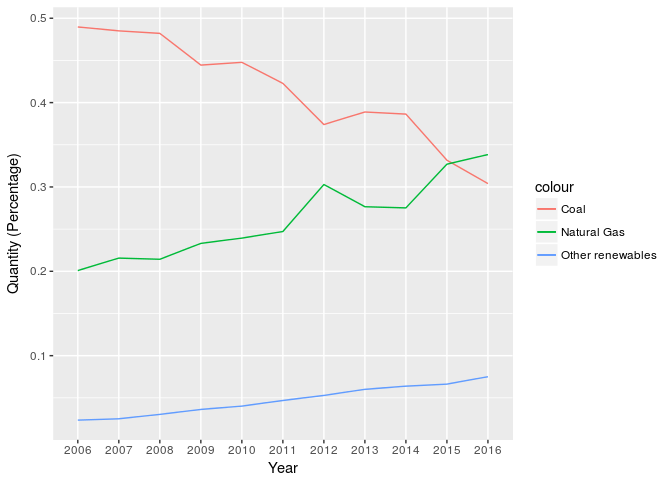
Coal vs Natural Gas
The following graph shows how coal is being replaced by natural gas and other renewables.
Carbon Dioxide Emissions by the Electricity Sector
In our period of interest the amount of carbon dioxide emitted by the electricity sector has been decreasing because of natural gas (which emits about 50% less than coal), and renewables (which does not emit any carbon dioxide).
